# Application
The app instance conventionally denotes the Fiber application.
#### New
Creates an new Fiber instance that we named "**app**".
```go
app := fiber.New()
// ...
// Application logic here...
// ...
app.Listen(8080)
```
#### Server
Fiber by default does not send a [server header](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Server), but you can enable this by changing the server value.
```go
app := fiber.New()
app.Server = "Windows 95"
// => Server: Windows 95
app.Listen(8080)
```
#### Banner
When you launch your Fiber application, the console will print a banner containing the package version and listening port. This is enabled by default, disable it by setting the Banner value to false.

```go
app := fiber.New()
app.Banner = false
app.Listen(8080)
```
#### Engine
You can edit some of the Fasthttp server settings via the Fiber instance.
Make sure that you set these settings before calling the [Listen](#listen) method. You can find the description of each value in [Fasthttp server settings](https://github.com/valyala/fasthttp/blob/master/server.go#L150)
**Only change these settings if you know what you are doing.**
```go
app := fiber.New()
// These are the default fasthttp settings
app.Engine.Concurrency = 256 * 1024
app.Engine.DisableKeepAlive = false
app.Engine.ReadBufferSize = 4096
app.Engine.WriteBufferSize = 4096
app.Engine.ReadTimeout = 0
app.Engine.WriteTimeout = 0
app.Engine.IdleTimeout = 0
app.Engine.MaxConnsPerIP = 0
app.Engine.MaxRequestsPerConn = 0
app.Engine.TCPKeepalive = false
app.Engine.TCPKeepalivePeriod = 0
app.Engine.MaxRequestBodySize = 4 * 1024 * 1024
app.Engine.ReduceMemoryUsage = false
app.Engine.GetOnly = false
app.Engine.DisableHeaderNamesNormalizing = false
app.Engine.SleepWhenConcurrencyLimitsExceeded = 0
app.Engine.NoDefaultContentType = false
app.Engine.KeepHijackedConns = false
// Start your app
app.Listen(8080)
```
#### Prefork
Prefork enables use of the **[SO_REUSEPORT](https://lwn.net/Articles/542629/)** socket option, which is available in newer versions of many operating systems, including DragonFly BSD and Linux (kernel version 3.9 and later). This will spawn multiple go processes listening on the same port.
NGINX has a great article about [Socket Sharding](https://www.nginx.com/blog/socket-sharding-nginx-release-1-9-1/), these pictures are taken from the same article.
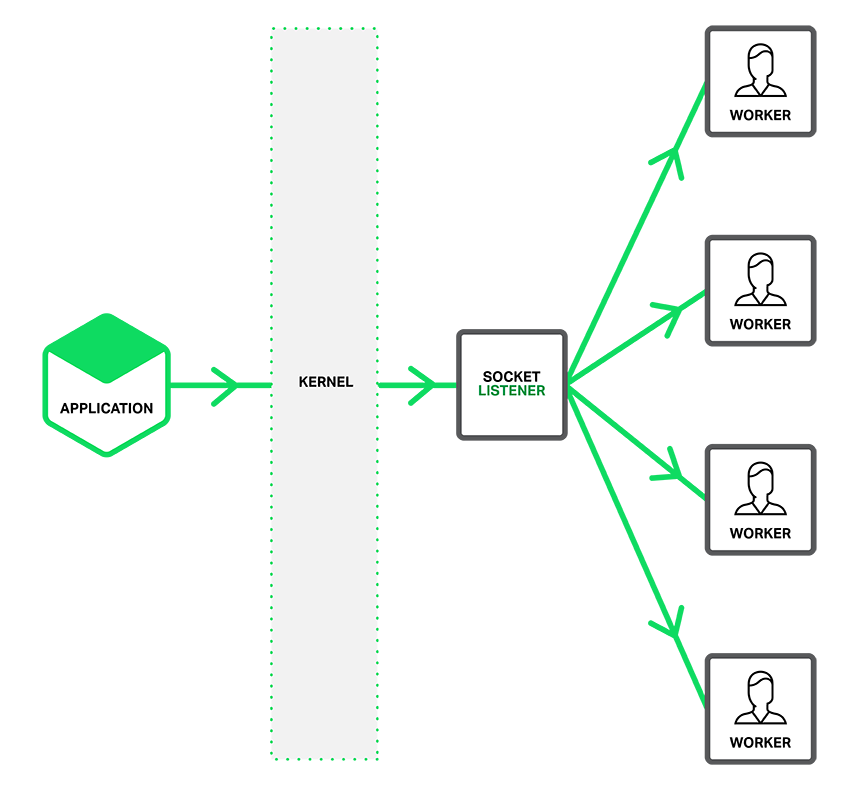
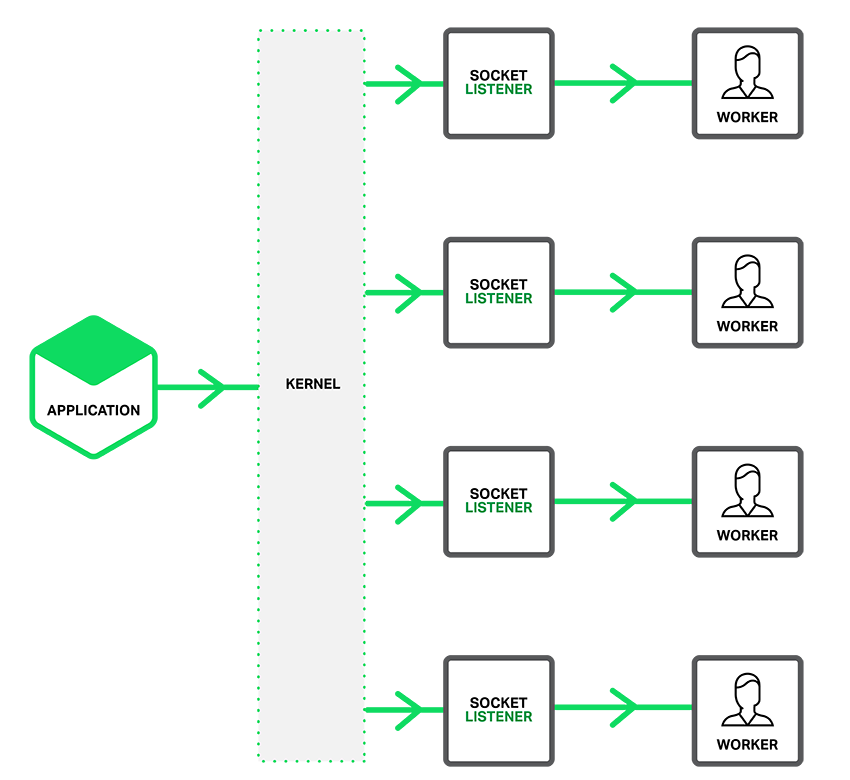 You can enable the **prefork** feature by adding the **-prefork** flag.
```bash
./server -prefork
```
Or enable the **Prefork** option in your app.
```go
app := fiber.New()
app.Prefork = true
app.Get("/", func(c *fiber.Ctx) {
c.Send(fmt.Sprintf("Hi, I'm worker #%v", os.Getpid()))
// => Hi, I'm worker #16858
// => Hi, I'm worker #16877
// => Hi, I'm worker #16895
})
app.Listen(8080)
```
#### Methods
Routes an HTTP request, where METHOD is the [HTTP method](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Methods) of the request, such as GET, PUT, POST, and so on capitalized. Thus, the actual methods are **app.Get()**, **app.Post()**, **app.Put()**, and so on.
```go
// Function signature
app.Get(handler func(*Ctx))
app.Get(path string, handler func(*Ctx))
// Methods
app.Connect(...)
app.Delete(...)
app.Get(...)
app.Head(...)
app.Options(...)
app.Patch(...)
app.Post(...)
app.Put(...)
app.Trace(...)
// Both All & Use matches all kind of HTTP request
// But there is a big difference
app.All(...) // Will match complete path with :params support
app.Use(...) // Will only see wheter url starts with specified path without :params support
```
#### Static
To serve static files such as images, CSS files, and JavaScript files, replace your function handler with a file or directory string.
By default this method will send `index.html` files in response to a request on a directory.
```go
// Function signature
app.Static(root string)
app.Static(prefix, root string)
```
For example, use the following code to serve images, CSS files, and JavaScript files in a directory named public:
```go
app.Static("./public")
```
Now, you can load the files that are in the public directory:
```shell
http://localhost:8080/hello.html
http://localhost:8080/js/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/css/style.css
```
To use multiple static assets directories, call the Static function multiple times:
```go
app.Static("./public")
app.Static("./files")
```
?>For best results, use a reverse proxy cache like [NGINX](https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/examples/reverseproxycachingexample/) to improve performance of serving static assets.
To create a virtual path prefix (where the path does not actually exist in the file system) for files that are served by the express.static function, specify a mount path for the static directory, as shown below:
```go
app.Static("/static", "./public")
```
Now, you can load the files that are in the public directory from the /static path prefix.
```shell
http://localhost:8080/static/hello.html
http://localhost:8080/static/js/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/static/css/style.css
```
#### Listen
Binds and listens for connections on the specified address. This can be a **INT** for port or **STRING** for address. To enable **TLS/HTTPS** you can append your **cert** and **key** path.
```go
// Function signature
app.Listen(address interface{}, tls ...string)
// Examples
app.Listen(8080)
app.Listen("8080")
app.Listen(":8080")
app.Listen("127.0.0.1:8080")
// Enable TLS/HTTPS
app.Listen(443, "server.crt", "server.key")
```
_Caught a mistake? [Edit this page on GitHub!](https://github.com/gofiber/fiber/blob/master/docs/application.md)_
You can enable the **prefork** feature by adding the **-prefork** flag.
```bash
./server -prefork
```
Or enable the **Prefork** option in your app.
```go
app := fiber.New()
app.Prefork = true
app.Get("/", func(c *fiber.Ctx) {
c.Send(fmt.Sprintf("Hi, I'm worker #%v", os.Getpid()))
// => Hi, I'm worker #16858
// => Hi, I'm worker #16877
// => Hi, I'm worker #16895
})
app.Listen(8080)
```
#### Methods
Routes an HTTP request, where METHOD is the [HTTP method](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Methods) of the request, such as GET, PUT, POST, and so on capitalized. Thus, the actual methods are **app.Get()**, **app.Post()**, **app.Put()**, and so on.
```go
// Function signature
app.Get(handler func(*Ctx))
app.Get(path string, handler func(*Ctx))
// Methods
app.Connect(...)
app.Delete(...)
app.Get(...)
app.Head(...)
app.Options(...)
app.Patch(...)
app.Post(...)
app.Put(...)
app.Trace(...)
// Both All & Use matches all kind of HTTP request
// But there is a big difference
app.All(...) // Will match complete path with :params support
app.Use(...) // Will only see wheter url starts with specified path without :params support
```
#### Static
To serve static files such as images, CSS files, and JavaScript files, replace your function handler with a file or directory string.
By default this method will send `index.html` files in response to a request on a directory.
```go
// Function signature
app.Static(root string)
app.Static(prefix, root string)
```
For example, use the following code to serve images, CSS files, and JavaScript files in a directory named public:
```go
app.Static("./public")
```
Now, you can load the files that are in the public directory:
```shell
http://localhost:8080/hello.html
http://localhost:8080/js/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/css/style.css
```
To use multiple static assets directories, call the Static function multiple times:
```go
app.Static("./public")
app.Static("./files")
```
?>For best results, use a reverse proxy cache like [NGINX](https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/examples/reverseproxycachingexample/) to improve performance of serving static assets.
To create a virtual path prefix (where the path does not actually exist in the file system) for files that are served by the express.static function, specify a mount path for the static directory, as shown below:
```go
app.Static("/static", "./public")
```
Now, you can load the files that are in the public directory from the /static path prefix.
```shell
http://localhost:8080/static/hello.html
http://localhost:8080/static/js/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/static/css/style.css
```
#### Listen
Binds and listens for connections on the specified address. This can be a **INT** for port or **STRING** for address. To enable **TLS/HTTPS** you can append your **cert** and **key** path.
```go
// Function signature
app.Listen(address interface{}, tls ...string)
// Examples
app.Listen(8080)
app.Listen("8080")
app.Listen(":8080")
app.Listen("127.0.0.1:8080")
// Enable TLS/HTTPS
app.Listen(443, "server.crt", "server.key")
```
_Caught a mistake? [Edit this page on GitHub!](https://github.com/gofiber/fiber/blob/master/docs/application.md)_

 You can enable the **prefork** feature by adding the **-prefork** flag.
```bash
./server -prefork
```
Or enable the **Prefork** option in your app.
```go
app := fiber.New()
app.Prefork = true
app.Get("/", func(c *fiber.Ctx) {
c.Send(fmt.Sprintf("Hi, I'm worker #%v", os.Getpid()))
// => Hi, I'm worker #16858
// => Hi, I'm worker #16877
// => Hi, I'm worker #16895
})
app.Listen(8080)
```
#### Methods
Routes an HTTP request, where METHOD is the [HTTP method](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Methods) of the request, such as GET, PUT, POST, and so on capitalized. Thus, the actual methods are **app.Get()**, **app.Post()**, **app.Put()**, and so on.
```go
// Function signature
app.Get(handler func(*Ctx))
app.Get(path string, handler func(*Ctx))
// Methods
app.Connect(...)
app.Delete(...)
app.Get(...)
app.Head(...)
app.Options(...)
app.Patch(...)
app.Post(...)
app.Put(...)
app.Trace(...)
// Both All & Use matches all kind of HTTP request
// But there is a big difference
app.All(...) // Will match complete path with :params support
app.Use(...) // Will only see wheter url starts with specified path without :params support
```
#### Static
To serve static files such as images, CSS files, and JavaScript files, replace your function handler with a file or directory string.
By default this method will send `index.html` files in response to a request on a directory.
```go
// Function signature
app.Static(root string)
app.Static(prefix, root string)
```
For example, use the following code to serve images, CSS files, and JavaScript files in a directory named public:
```go
app.Static("./public")
```
Now, you can load the files that are in the public directory:
```shell
http://localhost:8080/hello.html
http://localhost:8080/js/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/css/style.css
```
To use multiple static assets directories, call the Static function multiple times:
```go
app.Static("./public")
app.Static("./files")
```
?>For best results, use a reverse proxy cache like [NGINX](https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/examples/reverseproxycachingexample/) to improve performance of serving static assets.
To create a virtual path prefix (where the path does not actually exist in the file system) for files that are served by the express.static function, specify a mount path for the static directory, as shown below:
```go
app.Static("/static", "./public")
```
Now, you can load the files that are in the public directory from the /static path prefix.
```shell
http://localhost:8080/static/hello.html
http://localhost:8080/static/js/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/static/css/style.css
```
#### Listen
Binds and listens for connections on the specified address. This can be a **INT** for port or **STRING** for address. To enable **TLS/HTTPS** you can append your **cert** and **key** path.
```go
// Function signature
app.Listen(address interface{}, tls ...string)
// Examples
app.Listen(8080)
app.Listen("8080")
app.Listen(":8080")
app.Listen("127.0.0.1:8080")
// Enable TLS/HTTPS
app.Listen(443, "server.crt", "server.key")
```
_Caught a mistake? [Edit this page on GitHub!](https://github.com/gofiber/fiber/blob/master/docs/application.md)_
You can enable the **prefork** feature by adding the **-prefork** flag.
```bash
./server -prefork
```
Or enable the **Prefork** option in your app.
```go
app := fiber.New()
app.Prefork = true
app.Get("/", func(c *fiber.Ctx) {
c.Send(fmt.Sprintf("Hi, I'm worker #%v", os.Getpid()))
// => Hi, I'm worker #16858
// => Hi, I'm worker #16877
// => Hi, I'm worker #16895
})
app.Listen(8080)
```
#### Methods
Routes an HTTP request, where METHOD is the [HTTP method](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Methods) of the request, such as GET, PUT, POST, and so on capitalized. Thus, the actual methods are **app.Get()**, **app.Post()**, **app.Put()**, and so on.
```go
// Function signature
app.Get(handler func(*Ctx))
app.Get(path string, handler func(*Ctx))
// Methods
app.Connect(...)
app.Delete(...)
app.Get(...)
app.Head(...)
app.Options(...)
app.Patch(...)
app.Post(...)
app.Put(...)
app.Trace(...)
// Both All & Use matches all kind of HTTP request
// But there is a big difference
app.All(...) // Will match complete path with :params support
app.Use(...) // Will only see wheter url starts with specified path without :params support
```
#### Static
To serve static files such as images, CSS files, and JavaScript files, replace your function handler with a file or directory string.
By default this method will send `index.html` files in response to a request on a directory.
```go
// Function signature
app.Static(root string)
app.Static(prefix, root string)
```
For example, use the following code to serve images, CSS files, and JavaScript files in a directory named public:
```go
app.Static("./public")
```
Now, you can load the files that are in the public directory:
```shell
http://localhost:8080/hello.html
http://localhost:8080/js/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/css/style.css
```
To use multiple static assets directories, call the Static function multiple times:
```go
app.Static("./public")
app.Static("./files")
```
?>For best results, use a reverse proxy cache like [NGINX](https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/examples/reverseproxycachingexample/) to improve performance of serving static assets.
To create a virtual path prefix (where the path does not actually exist in the file system) for files that are served by the express.static function, specify a mount path for the static directory, as shown below:
```go
app.Static("/static", "./public")
```
Now, you can load the files that are in the public directory from the /static path prefix.
```shell
http://localhost:8080/static/hello.html
http://localhost:8080/static/js/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/static/css/style.css
```
#### Listen
Binds and listens for connections on the specified address. This can be a **INT** for port or **STRING** for address. To enable **TLS/HTTPS** you can append your **cert** and **key** path.
```go
// Function signature
app.Listen(address interface{}, tls ...string)
// Examples
app.Listen(8080)
app.Listen("8080")
app.Listen(":8080")
app.Listen("127.0.0.1:8080")
// Enable TLS/HTTPS
app.Listen(443, "server.crt", "server.key")
```
_Caught a mistake? [Edit this page on GitHub!](https://github.com/gofiber/fiber/blob/master/docs/application.md)_